Microsuction Ear Wax Removal (Aural Care)
Microsuction Ear Wax Removal (Aural Care)
AUDIOLOGY AND EAR WAX REMOVAL SERVICES
Symptoms suggesting the need for ear wax removal:

- Earache.
- Ear feeling blocked or full.
- Hearing loss which is getting worse.
- Edit Image
- Image of an Ear
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ear).
- Itching or discharge which may smell
How to use olive oil drops
1. Before bed, lie down on your side or tilt your head with the affected ear towards the ceiling.
2. Drop 2-3 drops of olive oil (at room temperature) into the canal (for stubborn wax, dissolve 1/2 teaspoon of baking soda in 60ml of warm water. Gently drip 5 to 10 drops).
3. Massage the hard piece at the front of the ear at the entrance of your ear canal (tragus).

4. Stay lying down, or keep head tilted, for 5 minutes, then wipe away any excess oil.
5. Do not put cotton wool into your ear afterwards as this will absorb the oil.
6. Continue to repeat the procedure on that ear only, as advised or until there
has been some improvement.
7. If the other ear is affected, begin treatment on that ear a few days after. You can contact us for a professional ear cleaning. For preventative treatment, begin treatment in the other ear 2 weeks following treatment in the first ear. Contact us for Ear infection treatment London
Post-treatment advice
- Your ear canal may be vulnerable to infection after microsuction and irrigation until the ear produces more wax to protect itself. So, it is important to keep your ears dry for a minimum of 4 to 5 days after the procedure.
- To keep the ears dry when you are washing your hair, we can discuss options for ear plugs.
- In the very unlikely event that you develop pain, dizziness, reduced hearing or discharge from the ear after the procedure, get in touch with your GP.
- Always seek medical advice if you experience sudden hearing loss or pain or discharge in your ear.
- If wax has been removed because you were experiencing hearing loss, we can check whether good hearing is restored after treatment, with a formal hearing assessment by the Audiologist. We also have Hearing tests for children
Causes of Impacted Wax:
- History of working or living in dusty environments.
- Using cotton buds, or any other object to clean the ear canal.
- Using ear plugs and earbud headphones.
- Using hearing aids.
- A history of frequent syringing and irrigation
Remember
- Ear wax is a natural build up of dead cells, hair, foreign material such as dust, and cerumen.
- Poking anything in your ear will only push the wax deeper and possibly cause problems and trauma to your ear.
- Keep hearing aids clean if you use them.
- To prevent build-up of excessive wax, if this is a regular problem for you, it may be helpful to put 1-2 drops of olive oil in your ears once or twice a month (instructions below).
- Normally ear wax causes no, or minimal symptoms but occasionally it can cause symptoms such as dulled hearing, earache or vertigo. If this occurs, please do see your GP or a pharmacist who can recommend ear wax drops. Alternatively, book an appointment with us.
Do not use wax softening agents if you think you could have a perforated eardrum.
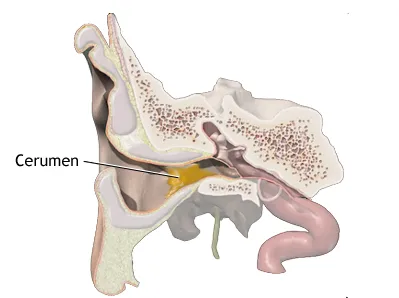
Cerumen, or wax as it is commonly known, is a normal secretion of the ceruminous glands in the outer meatus. It is slightly acidic, giving bactericidal qualities in both its wet, sticky form (as secreted by Caucasians and African-Caribbeans) or dry, flaky form (as, for example, secreted by S.E. Asian people). In addition to epithelial migration, jaw movement assists the movement of wax to the entrance of the External Auditory Meatus (EAM) where it emerges onto the skin.
A small amount of wax is normally found in the EAM and its absence may be a sign that dry skin conditions, infection or excessive cleaning have interfered with the normal production of wax. It is only when there is an accumulation of wax that removal may be necessary. A build-up of wax is more likely to occur in older adults and patients with learning difficulties, hearing aid users, people who insert implements into the ear or have a narrow EAM. A build-up of wax may also occur as a result of anxiety, stress and dietary or hereditary factors. Excessive wax should be removed before it becomes impacted, which can give rise to tinnitus, hearing loss, vertigo, pain and discharge.
